Evolution of Medical Device Technology
Over the last forty years, there has been a notable upsurge in technological progress in the realm of medical devices, leading to the rise of Software as a Medical Device (SaMD).
Accelerated Progress in Recent Years
In recent times, this progress has experienced a notable acceleration, largely attributed to the widespread adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT) and its associated elements. Elements such as wireless connectivity, cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and the utilization of SaMD have played pivotal roles in this acceleration.
Transformation in Healthcare Services
These innovations have not only revolutionized healthcare processes but also triggered a substantial transformation in the administration and delivery of healthcare services. They have redefined patient care, diagnostics, treatment monitoring, and overall healthcare management. The integration of these technologies has brought about significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility within the healthcare industry.
Understanding the Types of Software for Medical Devices
Software for medical devices can be classified into three main types:
Software as a Medical Device (SaMD)
Medical Device Software (SaMD) is software designed for medical applications, either independently or in combination with a medical device. Its functionalities encompass diagnosing, treating, monitoring, or preventing diseases and conditions. An example of SaMD is software that utilizes artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze medical images and identify conditions such as cancer or other diseases.
Software in a Medical Device (SiMD)
SiMD stands out as a significant category of software designed for medical devices, integrated within the device to ensure its safe and effective functionality. SiMD is responsible for managing the device’s hardware and executing essential functions. For instance, software governing the insulin flow in an insulin pump exemplifies the role of software within a medical device.
Applications employed in the production or upkeep of medical equipment.
Software employed in the creation or upkeep of medical devices serves purposes such as design, development, manufacturing, or maintenance. It is not intended for direct use by patients or healthcare providers. For instance, software utilized in the design of medical devices through computer-aided design (CAD) exemplifies the kind of software involved in the manufacturing or maintenance of medical devices.
How Do You Know If Your Mobile App is a SaMD?
The primary method of categorizing a mobile app as SaMD involves evaluating its intended function. According to FDA guidelines, if an app is used to cure, detect, treat, mitigate, or prevent diseases, it is deemed to be Software as a Medical Device (SaMD).
For instance, a glucose monitoring application that gathers blood sugar level data and stores it in cloud storage falls into this classification. Similarly, an application designed to oversee irregularities in EKG data qualifies as a medical device if its primary purpose is diagnostic.
FDA-approved documentation outlines the key criteria for Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) as follows:
- SaMD is considered a medical device and includes certain in-vitro diagnostic (IVD) medical devices.
- It is capable of operating on general-purpose (non-medical) computing platforms.
- Software does not fall under the SaMD definition if its primary purpose is to operate hardware medical devices.
- It can be used in conjunction with other products, such as medical devices.
- It can interface with various medical devices, encompassing hardware medical devices, other SaMD software, as well as general-purpose software.
Factors to Consider for SaMD Characterization
Establishing the purpose of SaMD is paramount for its classification. The definition statement serves as the foundation for categorizing SaMD, and the process relies extensively on the information furnished by the software. SaMDs undergo characterization through two distinct methods:
Information conveyed by SaMD includes:
- Facilitating patient diagnosis or treatment
- Providing insights for clinical management
- Guiding clinical management decisions
Health condition :
- Critical health condition
- Serious health condition
- Non-serious health condition
After information is delineated according to the aforementioned characterizations, SaMDs are categorized into four groups, ranging from I to IV.
Understanding the Software As a Medical Device Examples
SaMD represents a form of software that engages with diverse medical devices, encompassing both hardware and software, within clinical and general-use environments. For example, therapy planning software can furnish data to a linear accelerator, subsequently serving as input for another hardware device. This instance underscores the broad spectrum of applications for SaMD.
Yet another example of Software as a Medical Device involves software crafted for analyzing a condition utilizing a tri-axial accelerometer, functioning on the embedded processor within a consumer digital camera. This particular software qualifies as a Medical Device based on its intended capabilities for medical analysis.
Moreover, Software linked to a medical hardware device, yet not essential for the device to fulfill its medical purpose, is classified as Software as a Medical Device and not considered an accessory to the medical device.
Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) can operate on general-purpose computing platforms designed for non-clinical functions. When these software applications are installed on such platforms, they can also be seamlessly integrated into a hardware medical device.
Category Wise Examples of SaMD
As mentioned earlier, the risk-based categories of SaMD, categorized as IV, are elaborated below:
Category IV:
- SaMDs that conduct diagnostic image analysis to facilitate treatment decisions during acute stroke episodes.
- SaMDs compute the fractal dimension of a lesion and construct a structural map, unveiling distinct growth patterns for diagnostic purposes, and distinguishing between benign and malignant lesions.
- Software as a Medical Devices integrates data from immunoassays to screen for mutable pathogens outbreaks that may pose a high risk of contagion.
Category III:
- SaMD utilizes the phone’s microphone to identify interrupted breathing patterns during sleep.
- It is employed to offer information, such as capturing images, monitoring growth, or collecting additional data, to complement the information used by healthcare providers for diagnosing whether a skin lesion is benign or malignant.
Category II:
- SaMDs conducting heart rate analysis.
- SaMD utilizes individuals’ health record data to forecast the risks of heart disease or stroke and formulate preventive strategies.
- SaMD incorporates and analyzes various tests to provide diagnostic recommendations for specific clinical indications.
Category I:
- Medical software devices collect data from symptom diaries to offer insights for assessing the likelihood of an asthma episode.
- Medical software devices examining images and eye movement to direct subsequent diagnostic steps for astigmatism.
- Software storing historical blood pressure data for healthcare providers’ review.
- Software utilizing data on hearing sensitivity, speech in noise, and user responses to questionnaires on typical listening scenarios for self-assessment of hearing loss.
Exploring the Benefits of Software as a Medical Device
The domain of Software for Medical Devices is experiencing rapid growth, holding the potential to transform the landscape of healthcare delivery. SaMD solutions can deliver diverse advantages to patients, clinicians, and healthcare systems at large.
Benefits for Patients
Enhanced healthcare accessibility
SaMD can increase access to healthcare for individuals in remote or underserved regions, including those with disabilities.
Tailored healthcare
SaMD can gather and analyze patient data, offering more individualized recommendations for care.
Patient Empowerment
SaMD solution enables patients to take charge of their health by furnishing them with information and tools to oversee their conditions.
Enhanced Results
Software as a Medical Device solution can assist patients in enhancing their health outcomes by delivering real-time feedback and support.
Benefits for Clinicians
Enhanced efficiency
SaMD can automate tasks and workflows, allowing clinicians more time for patient interaction.
decision-making
SaMD solutions can offer clinicians data and insights to bolster their decision-making processes.
Enhanced patient care
Software as a Medical Device solution can assist clinicians in delivering improved patient care by equipping them with the necessary tools and information.
Benefits for Healthcare Systems
Cost reduction
contribute to reducing healthcare system costs through task automation, enhanced efficiency, and decreased hospital admissions.
Enhanced quality of care
Software as a Medical Device solution aids healthcare systems in elevating the quality of care by furnishing clinicians with the necessary tools and information for informed decision-making.
How Do You Ensure the Safety and Security of SaMD?
Ensuring the safety and security of Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) requires implementing several crucial measures. Let’s examine them in detail below:
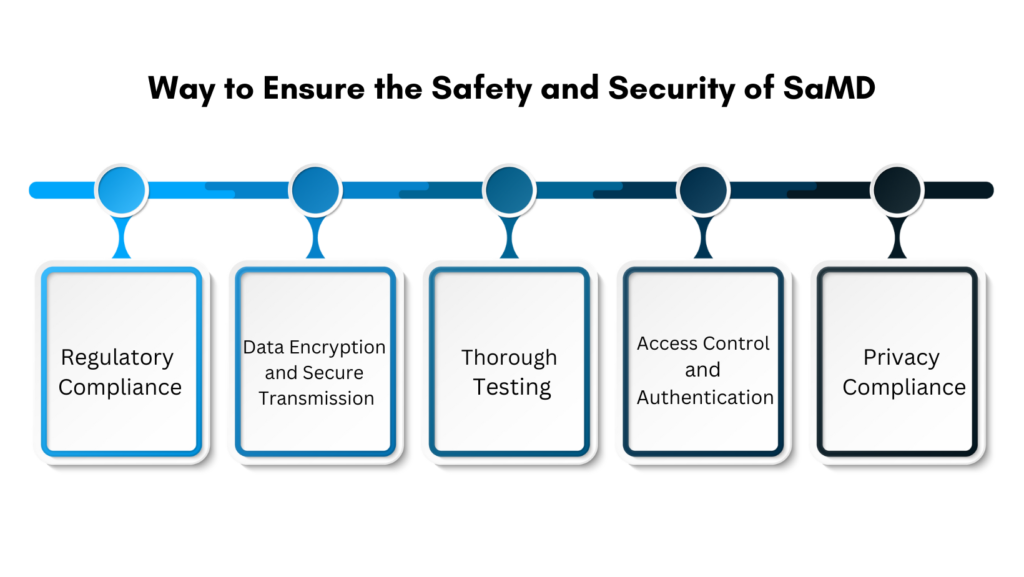
Regulatory Compliance
Validate that your software conforms to the applicable regulations and standards for Software as a Medical Device, by the guidelines set forth by the FDA and the EU MDR. Complying with these directives is imperative to ensure the safety and efficacy of your device for patient use.
Data Encryption and Secure Transmission
Implement encryption for patient data both at rest and during transmission to safeguard it against unauthorized access. This practice ensures the protection of patient data from unauthorized access, even in the event of interception by a hacker.
Thorough Testing
Comprehensive testing, encompassing validation and verification, is imperative to detect vulnerabilities and guarantee the precise and dependable performance of the SaMD. Rigorous testing serves to mitigate risks and bolster the overall reliability of the product.
Access Control and Authentication
Implement multi-factor authentication and user-centric access controls to limit data access exclusively to authorized users. The utilization of MFA and user-based access controls by SaMD manufacturers aids in safeguarding patient data against unauthorized access.
Privacy Compliance
To safeguard patient information, it is essential to adhere to privacy standards such as HIPAA in the United States. SaMD should ensure compliance with data protection laws and uphold patient confidentiality.
Future of Software as a Medical Device: Understanding the Trends and Innovations
following are upcoming trends in SaMD that can empower enterprises seeking innovative solutions:
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
The integration of AI is poised to profoundly influence SaMD, enabling advanced analysis, predictive diagnostics, and personalized treatments. Machine learning algorithms will augment SaMD’s capability to interpret data efficiently and provide precise diagnostic support.
Expansion of Telemedicine
rising embrace of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring will result in the heightened incorporation of Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) into these systems. SaMD solutions will play a pivotal role in facilitating remote diagnostics, continuous patient monitoring, and virtual health consultations, ultimately enhancing access to healthcare services.
Advancements in Wearable Devices
The progression of wearable technology in healthcare will persist, leading to the emergence of SaMD capable of analyzing data from smart wearables. These devices will gather health-related information, contributing to early diagnosis, continuous monitoring, and the management of chronic conditions.
Utilizing Blockchain for Data Security
Incorporating blockchain technology into SaMD to safeguard patient data will guarantee heightened security, transparency, and integrity of health records. This implementation will contribute to the improvement of patient privacy and data management in medical software.
Real Time Data Analytics
The real time data analytics of SaMD will provide healthcare providers with immediate insights, thereby improving diagnostic accuracy.
How Can Digiatto IT Services Help You With Healthcare Software Development?
Digiatto IT Services takes pride in possessing nearly a decade of experience in developing medical device software designed for medical applications. These software solutions operate autonomously, catering to a range of healthcare requirements, including diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment.
Our team of medical software developers can also create a frequency-based personal wellness system called Soniphi. It is a patient engagement platform that ensures every patient receives a remote monitoring care plan.
Talk to our experts to acquire a tailored Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) that aligns seamlessly with your business requirements.



Pingback: Role of Cloud Computing in Healthcare Industry - Health SaaS Pro
Pingback: Revolutionizing Healthcare Systems through Digital Innovation - Health SaaS Pro
Pingback: A Complete Guide to Healthcare Compliances - HealthSaaSPro
Pingback: Business Guide to Healthcare Application Development in 2024 - HealthSaaSPro